The Issue
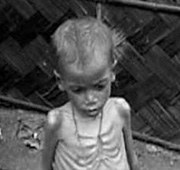 As shown in the previous lesson series, the denial of the right to food is not usually a result of natural causes, but due to systemic factors and deliberate actions taken by state authorities. In the same way, the systemic denial of other human rights ‘such as the right to equality or land’ will inevitably affect peoples?right to food.
As shown in the previous lesson series, the denial of the right to food is not usually a result of natural causes, but due to systemic factors and deliberate actions taken by state authorities. In the same way, the systemic denial of other human rights ‘such as the right to equality or land’ will inevitably affect peoples?right to food.
While human rights can be grouped into different categories, ultimately human rights are indivisible and must be viewed in a holistic manner, starting with the basic dignity of all people. Any practice that denies this basic dignity is inhuman, regardless whether the practice affects economic, social and cultural rights or civil and political rights.
The Lessons
This is the second of a two part lesson series. While the first (Lesson Series 38) focused on an introduction to the right to food as well as its conceptual framework, this second series looks at the indivisibility of rights.
Lesson 1: The relationship between caste discrimination and the right to food
Lesson 2: The relationship between the right to land and the right to food